Schemas as Single Sources of Truth
import { z, schema } from '@green-stack/schemas'In the Project Structure docs, we talked about how predictable patterns in folders and files can help you move faster through automation.
This guide explains how Zod based schemas can help you gain even more speed through a predictable way of defining your data shapes, when paired with tooling built around it:
A core feature of this universal starterkit is taking what works and making it better. This is why we invented schema() as a tiny wrapper around zod’s z.object(). You can use it to define your datastructures just once for the entire monorepo.
zodis a schema validation library built with Typescript in mind. By extending it withschema(), we can leverage its powerful features to create single sources of truth for GraphQL, API handlers, Database Models and even automatic component docs.
Why Single Sources of Truth?

The problem
Think about all the places you might need to redefine the structure of your data. Quite an extensive list for what is essentially describing the same data.
Generally speaking, you never want to define your data shape more than once. Not only is it redundant and a pain to do, it’s also a recipe for disaster.
If you need to change something, you have to remember to change it in all the places. If at any point you forget to do that, then you risk your datastructures getting out of sync. When that happens, it will likely lead to outdated editor hints or docs at best, and bugs or even crashes at worst.

The solution
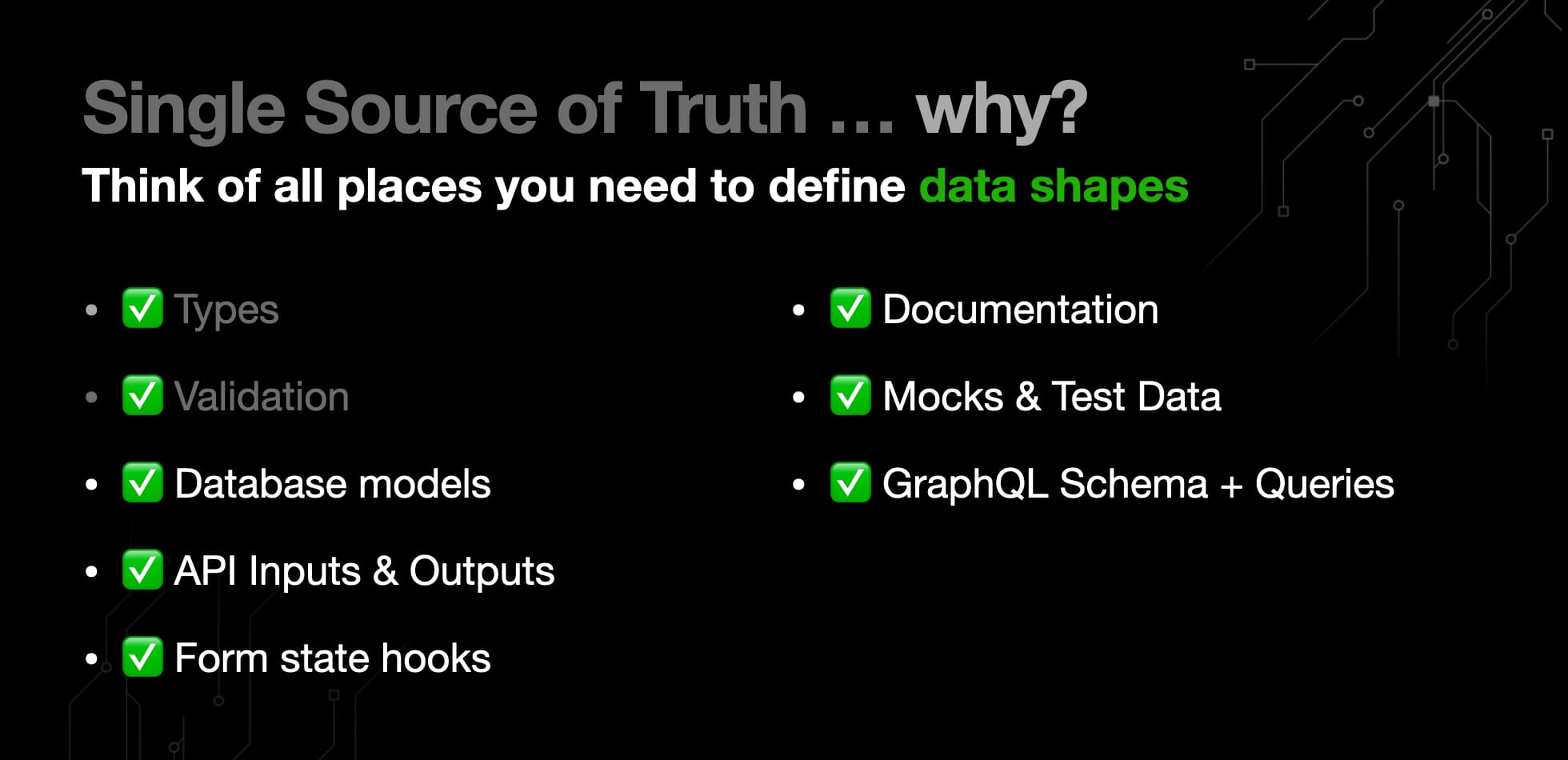
Now Imagine you can get all of this from just one schema:
- ✅ Types
- ✅ Validation + defaults
- ✅ DB models
- ✅ API inputs & outputs
- ✅ Form state
- ✅ Documentation
- ✅ Mock & test data
- ✅ GraphQL schema defs
You can use schema() to build out the shape of our data in one go. The resulting object will enable us to create all other definitions from it for (e.g.) GraphQL, DB models, docs and more. Meaning we can avoid ever declaring it again.
This is a huge win for maintainability and developer experience, as it avoids the need to keep it all in sync. No more redeclaring the same data shape for all your component props, database models or function args / responses.
Building Schemas with Zod
Let’s have a look at how zod and schema() defs translate to Typescript types: 👇
An object in this sense is a key-value pair, often used to represent the shape of a data “unit”:
some-workspace
└── /schemas/... # <- Single sources of truth
└── User.ts # <- e.g. User schemaexport const User = schema('User', {
// Requires a name value (☝️) to port to other formats later, keep it the same as your schema and TS type
// Zod can help you go even narrower than typescript
name: z.string().min(2), // <- e.g. Needs to be a string with at least 2 letters
age: z.number().min(18), // <- e.g. Age must be a number of at least 18
// Just like TS, it can help you indicate fields as optional
isAdmin: z.boolean().default(false), // <- Marked optional, defaults to false
birthdate: z.Date().nullish(), // = same as calling .nullable().optional()
})Check the full schema reference docs for all available way to build and describe schemas.
Extracting Types
The main thing to use schemas for is to hard-link validation with types.
You can extract the type from the schema using z.infer(), z.input() or z.output():
// Extract type from the schema and export it as a type alias
export type User = z.infer<typeof User>
// If you have defaults, you can use z.input() or z.output() instead
export type UserOutput = z.output<typeof User>
export type UserInput = z.input<typeof User>⬇⬇⬇
// {
// name: string,
// age: number,
// isAdmin?: boolean,
// birthDate?: Date | null,
// }In this case where we check the resulting type of
z.input(), the ‘isAdmin’ field will be marked as optional, as it’s supposedly not defaulted tofalseyet. If we’d inspectz.output(), it would be marked as required since it’s either provided or presumed defaulted.
Schema Validation
You can use the .parse() method to validate inputs against the schema:
// Call .parse() on the whole User schema...
const newUser = User.parse(someInput) // <- Auto infers 'User' type if valid
// ...or validate idividual fields by using '.shape' 👇
User.shape.age.parse("Invalid - Not a number")
// Throws => ZodError: "Expected a number, recieved a string."
// Luckily, TS will already catch this in your editor ( instant feedback 🙌 )If a field’s value does not match the schema, it will throw a ZodError:
try {
// 🚧 Will fail validation
const someNumber = z.number().parse("Not a number")
} catch (error) { // ⬇⬇⬇
/* Throws 'ZodError' with a .issues array:
[{
code: 'invalid_type',
expected: 'number',
received: 'string',
path: [],
message: 'Expected number, received string',
}]
*/
}Reusing and Expanding schemas
It can happen that you need to differentiate between two similar data shapes, for example, needing to expand on an existing shape.
- User.ts
- AdminUser.ts ← extension of 'User'
You can add new fields by calling .extendSchema() on the original schema:
// Extend the User schema
const AdminUser = User.extendSchema('AdminUser', {
isAdmin: z.boolean().default(true),
})
type AdminUser = z.infer<typeof AdminUser>
// {
// name: string,
// age: number,
// birthDate?: Date | null,
//
// isAdmin?: boolean, // <- New field added
// }You will need to provide a new name for the extended schema. This ensures there is no conflict with the original one when we port it to other formats.
There are other ways to create schemas from other ones, similar to how you would do it with Typescript:
.pickSchema()- to pick a subset of fields.omitSchema()- to remove a subset of fields
Defining Defaults
You can mark fields as optional or provide default values by using either:
.optional()- to allowundefined.nullable()- to allownull.nullish()- to allow both
You can also use .default() to provide a default value when the field isn’t passed in:
// Define a schema with optional and nullable fields
const User = schema('...', {
name: z.string().optional(), // <- Allow undefined
age: z.number().nullable(), // <- Allow null
birthData: z.date().nullish(), // <- Allow both
// Use .default() to make optional in args,
// but provide a default value when it IS undefined
isAdmin: z.boolean().default(false), // <- false
})When using
.default(), you might need to be more specifc when inferring types. You can usez.input()orz.output()to get the correct type. Based on which you choose, defaulted fields will be either optional or required.
Marking fields as sensitive
password: z.string().sensitive()In your schemas, you can mark fields as sensitive using .sensitive(). This will:
- Exclude the field from appearing in the GraphQL schema, introspection or queries
- Mark the field as strippable in API resolvers / responses (*)
- Mark the field with
isSensitive: truein schema introspection
Transforming to other formats
With both types and validation in place, you can now transform your schemas to other formats. This is where the real power of schema() comes into play.
Schema introspection
Before you can transform your schemas, you need to introspect them. This is done by calling .introspect() on the schema:
const userShapeMetadata = User.introspect()
// ⬇⬇⬇ Lists the JSON representation of your data shape
{
"name": "User",
"zodType": "ZodObject", // <- Zod class it was built with, e.g. z.object()
"baseType": "Object", // <- e.g. "Array" / "Boolean" / "String" / ...
"schema": {
// ☝️ Nested properties will be listed under "schema", e.g. object fields
"name": {
"zodType": "ZodString",
"baseType": "String",
"isOptional": false, // in case of .optional() or .default()
},
"age": {
zodType: "ZodNumber",
baseType: "Number", ...
},
"birthDate": {
zodType: "ZodDate",
baseType: "Date", ...
}
}
}Don’t worry though, you’re unlikely to have to do this manually in your day-to-day work.
A deep introspection API is what allows the kit to transform these zod schemas to other formats. Introspection is what enables schemas to serve as the Single Sources of Truth for all data shapes, making them quite portable.
Introspection metadata
This is all possible metadata you can extract with .introspect() from a single schema field:
type Metadata<S> = {
// Essentials
name?: string, // <- The name you passed to schema(), e.g. 'User'
zodType: ZOD_TYPE,
baseType: BASE_TYPE,
// Optionality and defaults
isOptional?: boolean,
isNullable?: boolean,
defaultValue?: any$Unknown,
// Documentation
exampleValue?: any$Unknown,
description?: string,
minLength?: number,
maxLength?: number,
exactLength?: number,
minValue?: number,
maxValue?: number,
// Flags
isInt?: boolean,
isBase64?: boolean,
isEmail?: boolean,
isURL?: boolean,
isUUID?: boolean,
isDate?: boolean,
isDatetime?: boolean,
isTime?: boolean,
isIP?: boolean,
// Literals, e.g. z.literal()
literalValue?: any$Unknown,
literalType?: 'string' | 'boolean' | 'number',
literalBase?: BASE_TYPE,
// e.g. Nested schema field(s) to represent:
// - object properties (like meta for 'age' / 'isAdmin' / ...)
// - array elements
// - tuple elements
schema?: S,
// The actual Zod object, only included with .introspect(true)
zodStruct?: z.ZodType & { ... }, // <- Outer zod schema (e.g. ZodDefault)
innerStruct?: z.ZodType & { ... }, // <- Inner zod schema (not wrapped)
// Mark as serverside only, strippable in API responses
isSensitive?: boolean,
// Compatibility with other systems like databases & drivers
isID?: boolean,
isIndex?: boolean,
isUnique?: boolean,
isSparse?: boolean,
}This is just to show how it works under the hood. You’re unlikely to need to use this directly in your day-to-day work.
Are you building your own tools that hook into the introspection result?
Then you can use these generic metadata types to help provide type-safety:
import type { Metadata, Meta$Schema, Meta$Tuple, ... } from '@green-stack/schemas'A good example of how introspected schemas can be transformed through is in the Automatic MDX Docs plugin:
Automatic MDX docgen
git merge with/automatic-docsThere’s two ways schemas are used to create docs:
- GraphQL schema comments provide hints in the GraphQL playground - at
/api/graphql - MDX component docs generated from the prop schema, with interactive controls
No. 1 already works without any plugin when using our recommended way to do GraphQL
No. 2 happens automatically when running
npm run devafter merging the docs plugin. (see demo)
For the best documentation experience, you’ll want to add some important metadata:
.describe()- to add a description to the field.example()- to provide an example value for previews / prop tables.default()- to provide a default value (also counts as example value)
Let’s say you have a component with props defined in a schema, like a <UserProfile /> component:
const UserProfileProps = schema('UserProfileProps', {
// Add a description to the field
name: z.string().describe('The name of the user'),
// Provide an example value
age: z.number().example(25),
// Add a description and example value
birthDate: z
.date()
.describe('User birthdate')
.example('1996-12-19'),
// Default values can be used as examples as well
isAdmin: z.boolean().default(false),
})
// Type alias
type UserProfileProps = z.infer<typeof UserProfileProps>
/* --- <UserProfile> --- */
export const UserProfile = (props: UserProfileProps) => {
// ...
}Export the prop introspection result from the same file. This links the props schema to the component so it gets picked up by the docs generator:
some-workspace
└── /components/...
└── UserProfile.tsx # <- export `getDocumentationProps`You can use .documentationProps() on the props schema. This will match export the introspection so it matches the expected format and provides hints to further refine your docs. It will call .introspect() internally to include the metadata we need to render in the preview + prop table:
// ...
/* --- Docs --- */
export const getDocumentationProps = UserProfileProps.documentationProps('UserProfile', {
// 🚧 All these options are optional:
valueProp: '...', // <- For form components, e.g. 'defaultValue', saved to docs URL state
onChangeProp: '...', // <- For form components, e.g. 'onTextChange', triggers save to URL state
// Alternative way to provide example props, e.g.:
exampleProps: {
name: 'John Doe',
age: 25,
birthDate: '1996-12-19',
isAdmin: false,
},
})Think of getDocumentationProps as a way to mark the component as documentable. It’s a convention that the docs plugin will look for when generating the MDX docs.
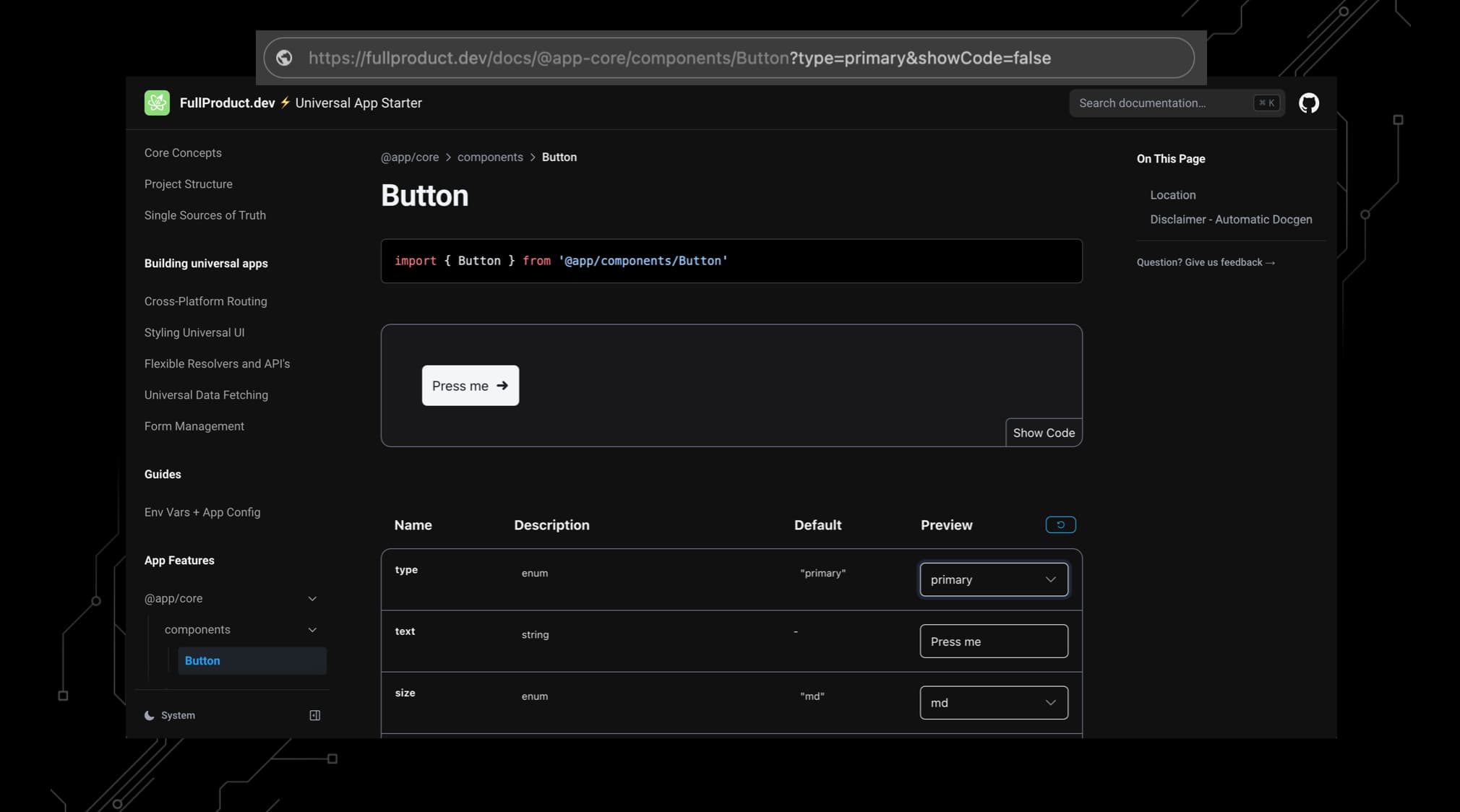
The end result will look like a Storybook-like documentation page for your component, with:
- ✅ Component name & import path
- ✅ Live preview of the component
- ✅ Props table with types, descriptions, examples, defaults
- ✅ Copyable component code for current prop settings
- ✅ Interactive controls to update both live preview, code example and URL
Check out a live example for the interactive Button component docs:
Custom Zod schema integrations
Out of the box:
npm run build:schema- Builds yourschema.graphqlfrom zod schemasbridgedFetcher()- Data fetcher that auto-scaffolds GraphQL query from zod input + output schemasuseFormState()- Form state hook to provide typed form state and validation utilscreateSchemaModel()- Createsmockmodel until merging any DB driver plugin 👇
In the near future, we will add plugin branches that further integrate zod schemas with DB and API solutions
Interactive DB driver plugins:
with/mongoose- zod to mongoosewith/supabase- zod to supabasewith/prisma- zod to prismawith/drizzle- zod to drizzlewith/airtable- zod to airtable
API plugins:
with/trpc- Pair zod Data Bridges with resolvers to create tRPC handlers
Note that these plugins are only available in the paid version of the starterkit.
Using introspection and the resulting metadata, you could also create your own custom integrations.
Schema generator
Like all elements of our recommended way of working, there is a Plop-based code generator to help create a schema in a specific workspace:
npm run add:schema⬇⬇⬇
will prompt you for a target workspace and name:
>>> Modify "your-project" using custom generators
? Where would you like to add this schema?
❯ @app/core # -- from features/app-core
some-feature # -- from features/some-feature
some-package # -- from packages/some-package⬇⬇⬇
>>> Modify "your-project" using custom generators
? Where would you like to add this schema? # @app/core
? What is the schema name? # SomeData
? Optional description? # ...
>>> Changes made:
• /features/@app-core/schemas/SomeData.ts # (add)
• Opened 1 file in VSCode # (open-in-vscode)
>>> Success!⬇⬇⬇
@app-core
└── /schemas/...
└── SomeData.schema.tsThough if you chose to also generate an integration, it might look like this instead:
@app-core
└── /schemas/...
└── SomeData.schema.ts
└── /hooks/...
└── useSomeData.ts # <- Form state hook using `useFormState()`
└── /models/...
└── SomeData.ts # <- `@db/driver` model using `createSchemaModel()`Pretty powerful, right?
Further reading
From our own docs:
- Data Bridges for fetching - Starterkit Docs
Relevant external resources:
- Zod’s official docs - zod.dev
- The Joy of Single Sources of Truth - Blogpost by Thorr ⚡️ @codinsonn.dev