
Cross-Platform Navigation + Routing
Workspace Defined Routes
We strongly recommend you define routes on the workspace level.
This way you can:
- ✅ Colocate routes with the rest of a feature’s domain (maximizes copy-paste-ability)
- ✅ Reuse them across platforms (auto re-exported to
@app/expoand@app/next)
features/@some-feature
└── /components/...
└── /screens/... # <- Reuses components
└── /HomeScreen.tsx
└── /routes/... # <- Reuses screens
└── /index.ts # <- Reuses e.g. 'HomeScreen.tsx'For an example of what this might look like in an actual project, check the example below. Don’t hesitate to click open some of the folders to get a better idea of how the routes are structured:
The recommended and easiest way to create a new route in a workspace is to use the Route Generator:
Using the Route Generator
npm run add:routeThe turborepo route generator will ask you some questions, like which url you’d like the route to have, and will generate the empty screens and routes folders in the workspace of your choosing, e.g.:
>>> Modify "your-project-name" using custom generators
? Where would you like to add this new route? # (Use arrow keys)
❯ features/@app-core -- importable from: '@app/core'
features/@some-feature -- importable from: '@app/some-feature'
features/@other-feature -- importable from: '@app/other-feature'⬇⬇⬇
>>> Modify "your-project-name" using custom generators
? Where would you like to add this new route? # -> features/@app-core
? What should the screen component be called? # -> NewRouteScreen
? What url do you want this route on? # e.g. "/examples/[slug]"
? Would you like to fetch initial data for this route from a resolver? # No data fetching
>>> Changes made:
• /features/@app-core/screens/NewRouteScreen.tsx # (add)
• /features/@app-core/routes/examples/[slug]/index.tsx # (add)
>>> Success!We’ll be ignoring providing initial data for now, but we’ll come back to it in Universal Data Fetching.
Manually adding universal routes
You could define your routes twice, once in
@apps/expoand once in@apps/next, in line with their way of working.
If you prefer to add routes manually, and like colocating to keep them portable, follow the steps below:
Add a screen component
Add a new screen component in a workspace /screens/ folder, e.g.:
// ...
/* --- <NewRouteScreen> -------------------- */
const NewRouteScreen = (props: ...) => {
// ...
}
/* --- Exports ----------------------------- */
export default NewRouteScreen
We’ll dive into how to best type the props for routes in the Universal Data Fetching docs.
Export screen in /routes/
You can use Next.js style routing conventions to export the screen component in the same workspace’s /routes/ folder, e.g.:
export { default } from '@app/core/screens/NewRouteScreen'
// -i- Export any other next.js routing config here
export const dynamic = 'auto'
export const dynamicParams = true
export const revalidate = false
export const fetchCache = 'auto'
export const runtime = 'nodejs'
export const preferredRegion = 'auto'
export const maxDuration = 5
Run npm run link:routes
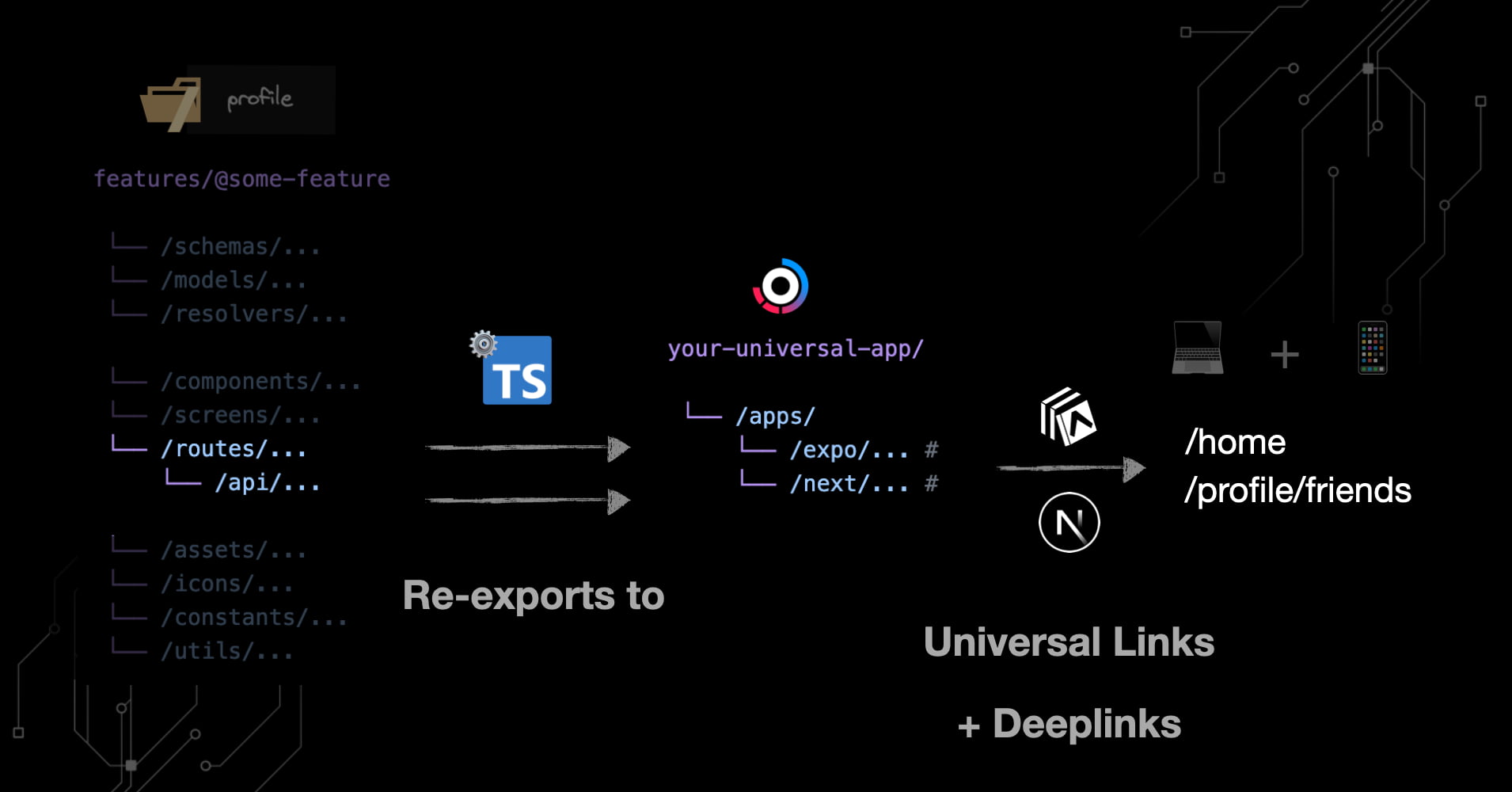
This command will automatically re-export all routes from the workspace to the platform-specific /app/ folder for Expo and Next.js
npm run link:routesThis deduplication will happen automatically when restarting with
npm run dev
⬇⬇⬇
Navigating pages
You can navigate using the useRouter hook or Link component from @green-stack/navigation. They provide APIs familiar to how navigation works in both the Next.js and expo-router app routers.
While they do use each platform’s underlying navigation system, they are not limited to just expo-router or next.js. Instead they will provide universal navigation utility.
Universal useRouter() hook
import { useRouter } from '@green-stack/navigation/useRouter'You can use router.push() to navigate to a new page:
const router = useRouter()
router.push('/examples/[slug]', '/examples/123')
.push()will use a push operation on mobile if possible.
There are also other methods available on the router object:
router.navigate()- Navigate to the provided hrefrouter.replace()- Navigate without appending to the historyrouter.back()- Go back in the historyrouter.canGoBack()- Check if there’s history that supports invoking theback()functionrouter.setParams()- Update the current route query params without navigating
Universal <Link/> component
If you import the Link component from @green-stack/navigation, it will automatically use the correct navigation system for the platform you are on.
import { Link } from '@green-stack/navigation'However, you can also import it from @app/primitives to apply tailwind styles:
import { Link } from '@app/primitives'You can use the href prop to navigate to a new page:
<Link
className="text-link p-2 rounded"
href="/examples/[slug]"
>
See example
</Link>UniversalLinkProps
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| children | React.ReactNode | The content to be rendered inside the link. |
| href | string | HREF | The path to route to on web or mobile. String only. Hints for internal routes provided through codegen. |
| style | Style prop: https://reactnative.dev/docs/text#style | |
| className | string | Nativewind classNames should be applied to either the parent or children of Link. Ideally, create or use a TextLink component instead. |
| replace | boolean | Should replace the current route without adding to the history - Default: false. |
| onPress | Extra handler that fires when the link is pressed. | |
| target | Specifies where to display the linked URL. | |
| asChild | boolean | Mobile only - Forward props to child component. Useful for custom buttons - Default: false. |
| push | boolean | Mobile only - Should push the current route, always adding to the history - Default: true. |
| testID | string | undefined | Mobile only - Used to locate this view in end-to-end tests. |
| nativeID | string | undefined | Mobile only - Used to reference react managed views from native code. @deprecated use id instead. |
| id | string | undefined | Mobile only - Used to reference react managed views from native code. |
| allowFontScaling | Mobile only - Specifies whether fonts should scale to respect Text Size accessibility settings. | |
| numberOfLines | Mobile only - Specifies the maximum number of lines to use for rendering text. | |
| maxFontSizeMultiplier | Mobile only - Specifies the maximum scale factor for text. | |
| suppressHighlighting | Mobile only - When true, no visual change is made when text is pressed down. | |
| scroll | boolean | Web only - Whether to override the default scroll behavior - Default: false. |
| shallow | boolean | Web only - Update the path of the current page without rerunning getStaticProps, getServerSideProps or getInitialProps - Default: false. |
| passHref | boolean | Web only - Forces Link to send the href property to its child - Default: false. |
| prefetch | boolean | Web only - Prefetch the page in the background. Any <Link /> that is in the viewport (initially or through scroll) will be preloaded. Prefetch can be disabled by passing prefetch={false}. When prefetch is set to false, prefetching will still occur on hover. Pages using Static Generation will preload JSON files with the data for faster page transitions. Prefetching is only enabled in production. - Default: true |
| locale | string | false | Web only - The active locale is automatically prepended. locale allows for providing a different locale. When false href has to include the locale as the default behavior is disabled. |
| as | Url | undefined | Web only - Optional decorator for the path that will be shown in the browser URL bar. |
Further reading
From our own docs:
Relevant external docs:
- Next.js Route segment config - Determine rendering & caching strategy per route
- Next.js Route Handlers - Used for Data Resolvers and API’s
- Expo Router and React Navigation - Used under the hood on mobile